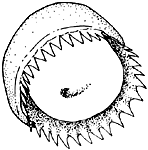
- Photophores (head)
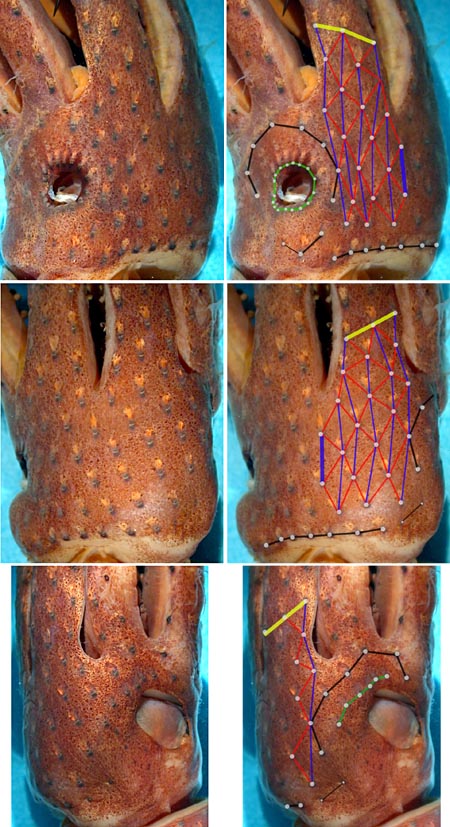
The right photograph of each pair below shows one or more of the basic photophore groups, from different views, with superimposed lines and dots to emphasize the photophore groups. The left photograph of each pair shows the same picture without superimposed lines and dots so that the photophores can be seen without obstruction. The superimposed lines are formed by first placing white dots over the pigmented, photogenic cups of all photophores in a particular group. The dots are then joined by a line of the appropriate color.
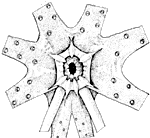
- Compound photophores (Type 2a):
- Basal Arm IV Row with 3 photophores. Medial photophore separated by 2 photophores from anterior photophore of Midline Series.
- Midline Series with 2 photophores.
- Right Eyelid Series with 17 photophores (occasionally 16: Voss, et al.,1998) .
- Left Eyelid Series with 6 photophores.
- 2° Right Eyelid Series with 8 photophores.
- 2° Left Eyelid Series with 7 photophores.
- Ventral Matrix with 42 photophores; 11 longitudinal (thin blue) series; attachment to 2° Eyelid Series at 2° eyelid photophores no. 2 on either side.
- Ventral Matrix photophores tend to align in transverse rows.
- Right basal series with 2 photophores.
- Left basal series with two very small photophores.
- Basal row smooth alignment with 7 photophores .
- Right Accessory Series with 2 photophores.
- Left Accessory Series with 3 photophores (one small).
- Simple photophores (round, black dots):
- Arrangement not investigated.
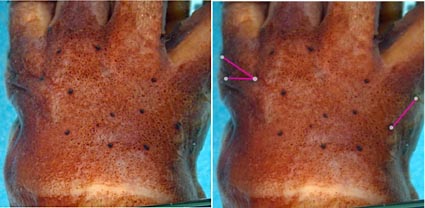
- Relatively large, simple photophores on dorsal surface of head (see illustration below).
- Small, simple photophores not easy to recognize and may be variable.
- Compound photophores (Type 2a):
- Compound photophores (mantle)
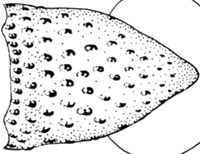
- Compound photophores of uniformly large size on anterior half of ventral mantle.
- Compound photophores (arms)
- Arms IV with 3 longitudinal series on arm base.
- Photophores on Arm IV tips not separated by a distinct gap from other arm photophores.
- Tentacles
- Club manus with 5-6 irregular series of suckers.
- Sucker series decreases to 2-3 near distal end of dactylus.
- Largest suckers 1.5-2.0 times larger than suckers of marginal series. Difference less in large squid.
- Arms
- Nearly subequal, 2=>3.1.4; length 100-200% of ML.
- Nearly subequal, 2=>3.1.4; length 100-200% of ML.
- Sucker dentition
- Sucker rings on arms IV with many low, square teeth on entire margin or only on distal margin.
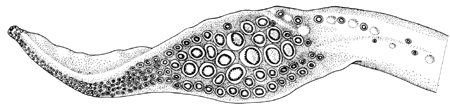
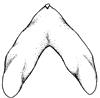
- Rings on enlarged median suckers of manus with 33-38 triangular or narrow pointed teeth (see drawing).
- Web and buccal crown
- Inner web 10-25% of length of longest arm. Outer web absent.
- Buccal crown with 7 supports.
- Funnel organ
- Dorsal pad unsculptured and appearing swollen or deflated.
- Fins
- Length 34-42% of ML; width 57-64% of ML.
- Length 34-42% of ML; width 57-64% of ML.
- Spermatophores
- Length 2.5-3.3% of ML; sperm mass 4-12% of spermatophore length (SpL), convoluted; cement body 57-72% of SpL; ejaculatory apparatus 25-37% of SpL and with one or two loops; connective complex absent.
- Length 2.5-3.3% of ML; sperm mass 4-12% of spermatophore length (SpL), convoluted; cement body 57-72% of SpL; ejaculatory apparatus 25-37% of SpL and with one or two loops; connective complex absent.
- Hectocotylus
- In mature males, pedestals of small suckers on ends of arm I swollen and elongate.
Comments
Except for the examination of the compound photophores of the head, the above description is from Voss et al., 1998 and Voss, 1969. We have found no differences in the arrangement of compound photophores of the head between H. corona and H. cerasina.






 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site